09. Physical Principles of CT Scanners
heading
Getting technical
In this and the following section, let’s get a bit more technical and try to understand how the data from 3D imaging modalities (the clinical term for “scanner”) is produced.
ND320 C3 L1 08 Ivan Intro
Physical Principles of CT scanner Heading
Physical Principles of operation of a CT scanner
Let’s take a look at what is a CT scanner and how it operates
ND320 C3 L1 09 Physical Principles Of CT Scanner
X-rays
X-rays
The main operating agents of a CT scanner are X-rays, which are a form of electromagnetic radiation. A reminder on electromagnetic spectrum below:
X-rays
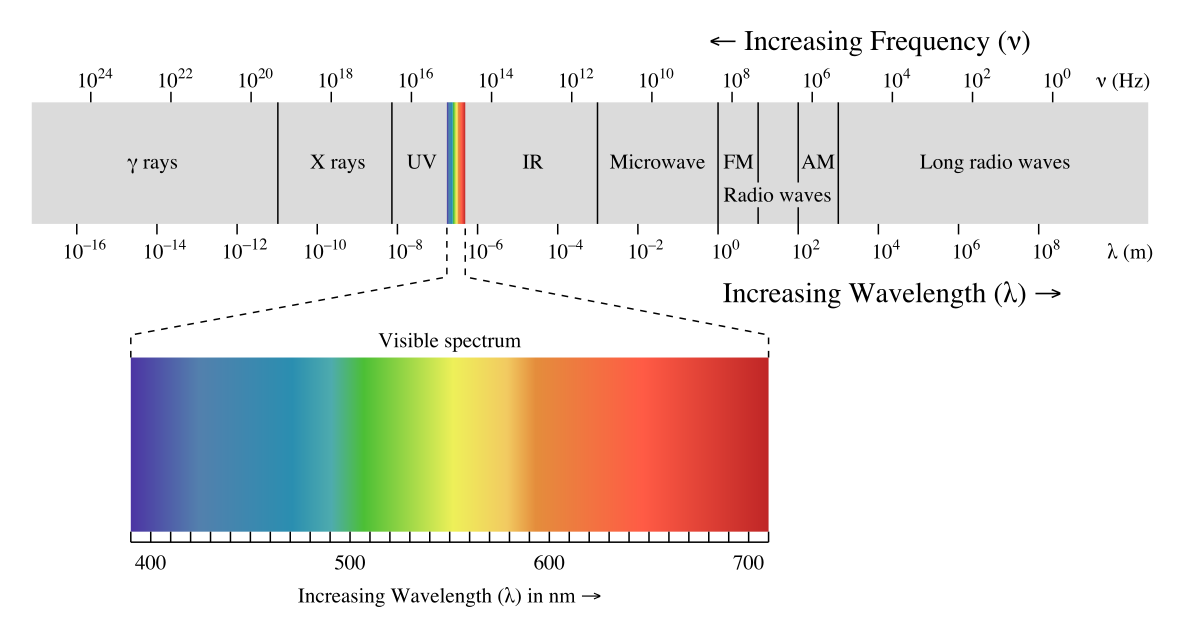
Electromagnetic spectrum
Physical Principles of CT Scanners
X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation, which means that they carry enough energy to detach electrons from atoms. This presents certain health risks, but the short wavelength of this part of the electromagnetic spectrum allows the radiation to interact with the many structures that compose a human body, thus allowing us to measure the amount of photons that reach detectors and make deductions about the structures that were in the way of photons as they were traveling from the source to the detector, with a high precision.
CT scanners
As you have seen, the CT scanner operates by projecting X-rays through the subject’s body.
X-rays get absorbed or scattered by the anatomy and thus detectors measure the amount of this attenuation that happens along each path that the ray is taking. A collimator shapes the beam and ensures that the X-rays only pass through a narrow slice of the object being imaged. Rotation of a source inside a gantry makes sure that projections happen from different angles so that we can get a good 2D representation of the slice. The moving table ensures that multiple such slices are imaged. A collection of slices makes up a 3-dimensional CT image.
In the exercise that follows we will look closer at how the formation of 2D slices works in a CT scanner.
Acting agent of a CT scanner
SOLUTION:
- Photons
- Electromagnetic waves
- X-rays
Summary & Vocab
New Vocabulary
- CT scanner: computed tomography scanner